As a point source of light is submerged, it embarks on a journey through diverse mediums, encountering unique challenges and exhibiting fascinating behaviors. This exploration delves into the characteristics, applications, and design considerations of submerged point sources, shedding light on their significance in various fields.
When a point source of light is submerged, it interacts with the surrounding medium, leading to intriguing phenomena such as light attenuation and scattering. These effects are influenced by factors like the wavelength of light and the properties of the medium, shaping the behavior of the light source in captivating ways.
Definition and Characteristics
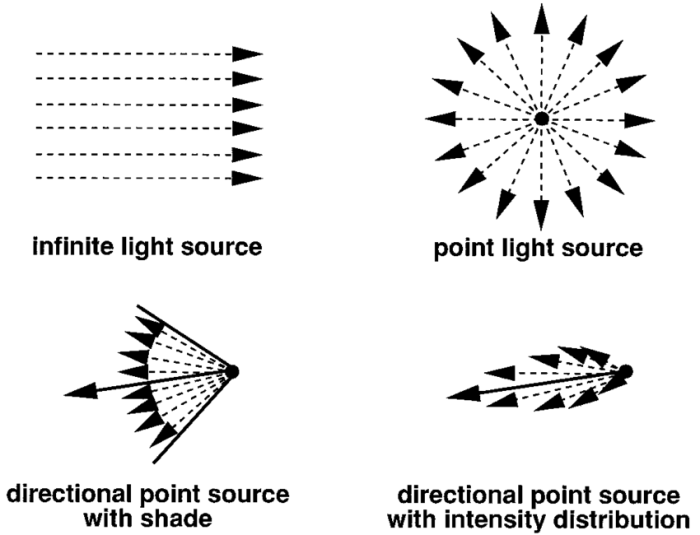
A point source of light is an idealization of a light source that emits light from a single, infinitesimally small point. In reality, all light sources have some finite size, but the point source approximation can be useful in many situations.
The properties and characteristics that distinguish a point source from other light sources include:
Properties of a Point Source
- Emits light from a single, infinitesimally small point.
- Light intensity decreases with the square of the distance from the source (inverse square law).
- Produces a spherical wavefront.
Characteristics of a Point Source
- Appears as a point of light from all directions.
- Casts sharp shadows with well-defined edges.
- Can be used to create collimated beams of light.
Submersion in Different Mediums
When a point source of light is submerged in a medium, the behavior of the light is affected by the properties of the medium. The speed of light, the direction of propagation, and the intensity of the light can all be affected by the medium in which the light is submerged.
Some examples of different mediums in which a point source of light can be submerged include:
- Air
- Water
- Glass
- Plastic
The speed of light in a medium is determined by the refractive index of the medium. The refractive index is a measure of how much the medium bends light. The higher the refractive index, the slower the speed of light in the medium.
The direction of propagation of light in a medium is determined by the angle of incidence of the light on the medium. The angle of incidence is the angle between the incoming light ray and the normal to the surface of the medium.
The normal is a line perpendicular to the surface of the medium.
The intensity of light in a medium is determined by the absorption and scattering of light by the medium. Absorption is the process by which light is absorbed by the medium, while scattering is the process by which light is scattered by the medium.
Light Attenuation and Scattering: A Point Source Of Light Is Submerged
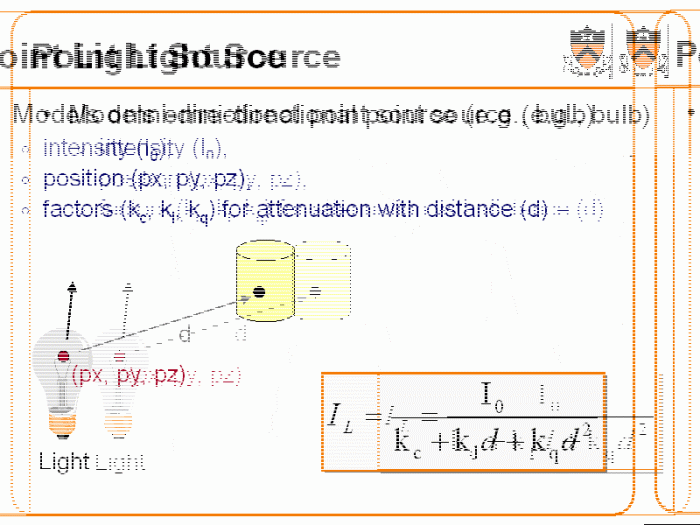
When a point source of light is submerged in a medium, the light undergoes attenuation and scattering. Attenuation refers to the decrease in light intensity as it travels through the medium, while scattering refers to the change in the direction of light propagation due to interactions with particles in the medium.
Mechanisms of Light Attenuation and Scattering
The mechanisms of light attenuation and scattering in submerged media are primarily determined by the interaction of light with the molecules and particles present in the medium. Light attenuation occurs due to absorption and scattering. Absorption is the process by which light energy is absorbed by the medium, while scattering is the process by which light is redirected in different directions due to interactions with particles.
Scattering can be further classified into two types: Rayleigh scattering and Mie scattering. Rayleigh scattering occurs when the size of the scattering particles is much smaller than the wavelength of light. In this case, the scattering is predominantly in the forward direction, resulting in a decrease in the intensity of the light beam.
Mie scattering occurs when the size of the scattering particles is comparable to or larger than the wavelength of light. In this case, the scattering is more complex and can result in both forward and backward scattering. The intensity of the scattered light depends on the size, shape, and refractive index of the scattering particles.
Factors Influencing Attenuation and Scattering
The degree of light attenuation and scattering in submerged media is influenced by several factors, including:
- Wavelength of light:Shorter wavelengths (e.g., blue light) are more susceptible to scattering than longer wavelengths (e.g., red light).
- Concentration and size of particles:Higher concentrations of particles and larger particle sizes increase the probability of scattering and absorption.
- Refractive index of the medium:The refractive index of the medium affects the amount of light scattered and absorbed.
- Path length:The longer the path length of light through the medium, the greater the attenuation and scattering.
Applications and Use Cases
Submerged point sources of light find applications in various fields, including underwater photography, marine biology, and underwater exploration.The unique characteristics of these light sources contribute to their effectiveness in these applications. Their ability to penetrate water effectively allows for clear and well-lit images in underwater photography.
In marine biology, they enable researchers to observe and study marine life in their natural habitat. Submerged point sources of light also enhance visibility and safety during underwater exploration and diving operations.
Underwater Photography
In underwater photography, submerged point sources of light provide targeted illumination, enhancing the quality of images captured underwater. The focused beam of light illuminates the subject, reducing the effects of scattering and backscatter, resulting in sharper and clearer images.
Marine Biology
Submerged point sources of light are essential for marine biology research. They allow researchers to observe and study marine life in their natural habitat without disturbing their behavior. The controlled illumination provided by these light sources enables researchers to observe specific species and their interactions with their environment.
Underwater Exploration
Submerged point sources of light enhance visibility and safety during underwater exploration and diving operations. They illuminate underwater environments, making it easier for divers to navigate and explore. These light sources also provide a beacon of light in case of emergencies, helping divers to find their way back to the surface.
Design Considerations for Submerged Point Sources
The design of submerged point sources of light requires careful consideration to optimize performance and minimize attenuation. Several key factors influence the design, including the choice of light source, optical design, and materials.
One of the primary design considerations is the selection of the light source. The type of light source used will impact the spectral output, intensity, and beam characteristics of the point source. Factors to consider when selecting a light source include the desired wavelength range, power requirements, and environmental conditions.
Optical Design
The optical design of the point source plays a crucial role in controlling the light distribution and minimizing attenuation. The optical system should be designed to maximize the light output in the desired direction while minimizing losses due to scattering and absorption.
The shape and size of the optical elements, as well as the materials used, can significantly impact the optical performance. Factors to consider when designing the optical system include the beam angle, uniformity, and efficiency.
Materials, A point source of light is submerged
The choice of materials for the point source is critical to ensure durability and minimize attenuation. The materials used must be compatible with the surrounding environment and resistant to corrosion and degradation.
The refractive index of the materials used in the optical system can also affect the light transmission and attenuation. Matching the refractive index of the materials can help reduce losses due to reflection and refraction.
Advanced Techniques and Future Directions
The field of submerged point sources is constantly evolving, with new techniques and developments emerging to enhance their performance and capabilities. Advanced techniques include the use of high-power LEDs, advanced optical designs, and novel materials.
High-power LEDs offer several advantages for submerged point sources, including high efficiency, long lifespan, and compact size. Advanced optical designs can optimize the light distribution and reduce losses, resulting in improved beam quality and increased underwater visibility. Novel materials, such as nanomaterials and metamaterials, can enhance light transmission and scattering, leading to improved performance in various applications.
Future Research Directions
Ongoing research and development efforts are focused on further improving the performance and capabilities of submerged point sources. Key areas of investigation include:
- Developing more efficient and reliable high-power LEDs
- Optimizing optical designs for improved beam quality and reduced losses
- Exploring novel materials and nanotechnologies to enhance light transmission and scattering
- Investigating new applications and use cases for submerged point sources
These advancements will continue to drive the development of submerged point sources and expand their applications in various fields.
FAQ
What is the primary characteristic of a point source of light?
A point source of light emits light from a single, infinitesimal point, creating rays that diverge in all directions.
How does submersion affect the intensity of light from a point source?
Submersion in a medium causes light attenuation, reducing the intensity of light due to absorption and scattering by the medium’s particles.
What factors influence the degree of light scattering when a point source is submerged?
Factors like the wavelength of light, the refractive index of the medium, and the size and concentration of particles in the medium affect the extent of light scattering.