Molecular genetics of color mutations in rock pocket mice sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. This exploration delves into the genetic mechanisms that govern color variation in these fascinating creatures, revealing the intricate interplay between genes and environment in shaping their unique adaptations.
Through the lens of molecular genetics, we embark on a journey to unravel the genetic basis of color mutations in rock pocket mice, identifying the key genes involved and exploring their functions and interactions. We delve into the potential influence of environmental factors on the occurrence and frequency of these mutations, examining how gene expression and color variation may be modulated by external stimuli.
Introduction: Molecular Genetics Of Color Mutations In Rock Pocket Mice
Molecular genetics provides a powerful tool for understanding the genetic basis of color mutations in rock pocket mice. These mice exhibit a remarkable range of color variation, and molecular studies have shed light on the genetic mechanisms responsible for these differences.
Rock pocket mice are small, nocturnal rodents found in the arid regions of North America. They are characterized by their distinctive color patterns, which vary from pale cream to dark brown. These color differences are primarily determined by mutations in genes involved in the production of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin and hair color.
Genetic Basis of Color Mutations
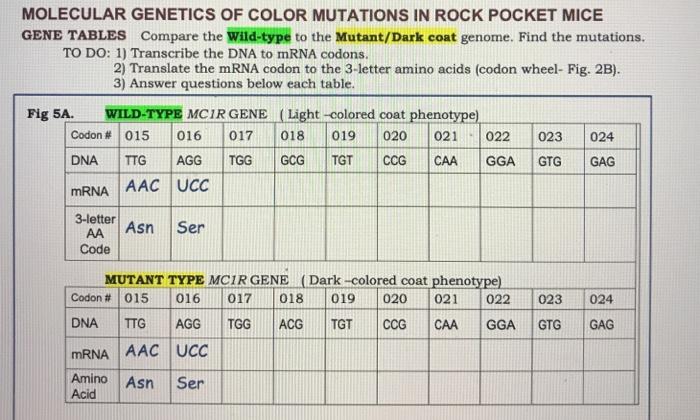
The genetic basis of color mutations in rock pocket mice has been extensively studied. Several genes have been identified as playing a role in these mutations, including the melanocortin-1 receptor( MC1R) gene and the agoutigene.
The MC1Rgene encodes a receptor for melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH), a hormone that regulates melanin production. Mutations in this gene can lead to changes in MSH signaling, resulting in alterations in melanin production and color variation.
The agoutigene encodes a protein that inhibits melanin production. Mutations in this gene can lead to decreased melanin production, resulting in lighter coat colors.
Environmental Influences on Color Mutations
In addition to genetic factors, environmental factors can also influence the occurrence and frequency of color mutations in rock pocket mice. These factors include temperature, humidity, and diet.
Temperature has been shown to affect the expression of the MC1Rgene. Higher temperatures can lead to increased MSH signaling and increased melanin production, resulting in darker coat colors.
Humidity and diet can also affect color variation in rock pocket mice. Low humidity and a diet high in carotenoids can lead to increased melanin production and darker coat colors.
Evolutionary Implications of Color Mutations
Color mutations in rock pocket mice have important evolutionary implications. These mutations can affect the survival and reproductive success of individuals by influencing their camouflage and thermoregulation.
In habitats with high levels of predators, darker coat colors may provide camouflage and reduce the risk of predation. In habitats with high temperatures, lighter coat colors may reflect more sunlight and reduce heat absorption.
Color mutations can also affect mate choice and reproductive success. Certain color patterns may be preferred by potential mates, leading to increased reproductive opportunities.
Applications in Conservation and Management

Understanding the molecular basis of color mutations in rock pocket mice has important applications in conservation and management. This knowledge can help inform conservation strategies and habitat preservation efforts.
By identifying the genes responsible for color variation, conservationists can develop genetic markers to track the distribution and abundance of different color morphs. This information can be used to monitor population health and identify areas of concern.
Additionally, understanding the environmental factors that influence color variation can help managers develop habitat management strategies that promote the survival and success of rock pocket mice with different color patterns.
Questions Often Asked
What are the key genes involved in color mutations in rock pocket mice?
Key genes include Mc1r, Agouti, and Asip, which play crucial roles in regulating melanin production and distribution.
How do environmental factors influence color mutations in rock pocket mice?
Environmental variables such as temperature, light exposure, and diet can affect gene expression and color variation.
What are the evolutionary implications of color mutations in rock pocket mice?
Color mutations may have contributed to their adaptation to different habitats, providing camouflage and enhancing mate selection.