Radioactive wastes are stored in a spherical stainless steel for several compelling reasons. This article delves into the intricacies of this storage method, exploring its advantages, safety measures, and environmental implications.
Stainless steel offers exceptional resistance to corrosion and leakage, making it an ideal material for containing radioactive waste. The spherical shape provides optimal surface area for heat dissipation, minimizing the risk of accidents.
Storage and Containment: Radioactive Wastes Are Stored In A Spherical Stainless Steel
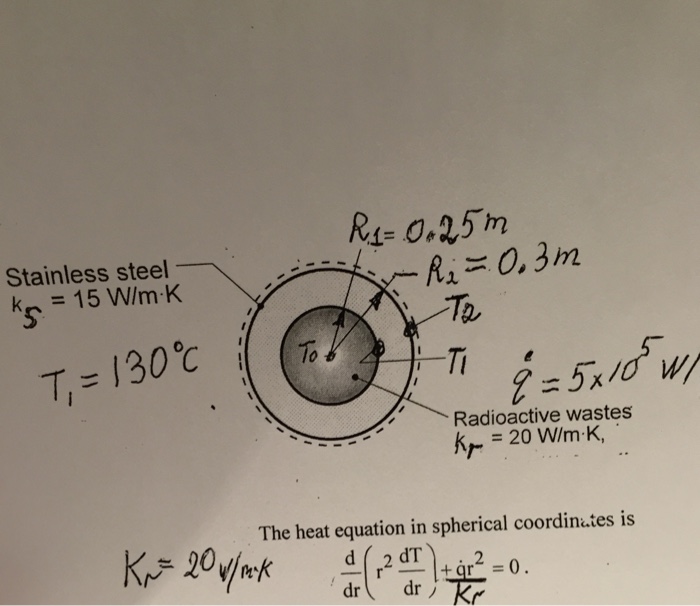
Radioactive waste is stored in spherical stainless steel containers due to its exceptional corrosion resistance and ability to withstand extreme conditions.
Spherical containment provides several advantages: it minimizes surface area, reducing potential leakage points; evenly distributes stress, enhancing structural integrity; and facilitates remote handling and transportation.
Alternative materials used for radioactive waste storage include concrete, lead, and polymers. Cylindrical and rectangular containers are also employed, but spherical shapes are generally preferred for their safety and efficiency.
Safety and Risk Assessment
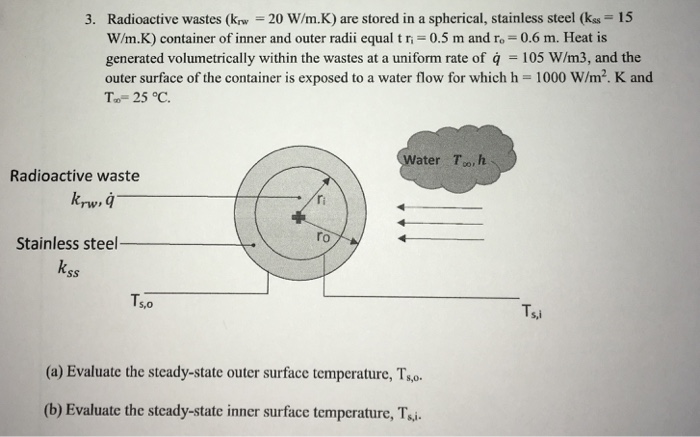
Safety measures for radioactive waste storage include multiple layers of containment, continuous monitoring systems, and emergency response plans.
Potential risks include leakage, accidents, and radiation exposure. Mitigation measures involve proper handling, robust containment structures, and comprehensive training for personnel.
Long-term monitoring and maintenance are crucial to ensure the integrity of storage facilities and prevent environmental hazards.
Environmental Impact

Radioactive waste storage poses potential environmental impacts, such as groundwater contamination and radiation exposure.
Regulations and guidelines aim to minimize these impacts through proper siting, containment design, and monitoring programs.
Successful waste management practices include geological repositories, where waste is stored deep underground in stable rock formations.
Disposal Options
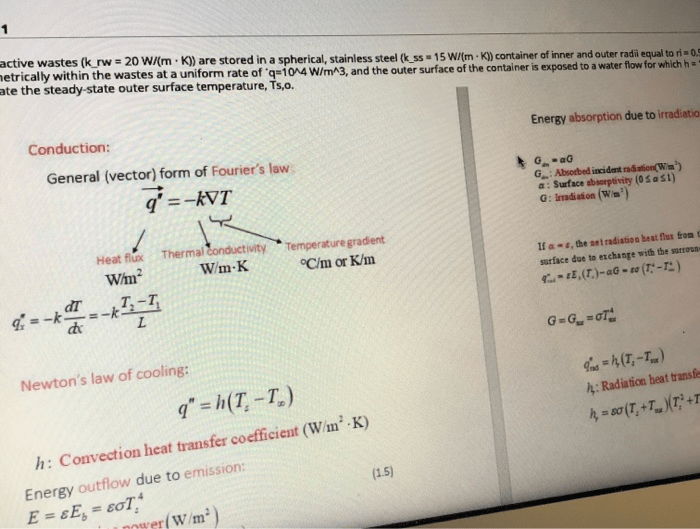
Disposal options for radioactive waste include deep geological repositories and reprocessing.
Deep geological repositories involve burying waste deep underground in stable geological formations, while reprocessing aims to extract reusable materials from the waste.
The choice of disposal method depends on factors such as waste type, volume, and safety considerations. Research and development continue to explore innovative disposal technologies.
Detailed FAQs
Why is stainless steel used for radioactive waste storage?
Stainless steel is highly resistant to corrosion and leakage, ensuring the safe containment of radioactive materials.
What are the advantages of spherical containment for radioactive waste?
Spherical containment provides optimal surface area for heat dissipation, reducing the risk of accidents.
What safety measures are in place to prevent leaks or accidents?
Multiple layers of containment, monitoring systems, and emergency response plans are implemented to minimize the risk of leaks or accidents.
What are the potential environmental impacts of radioactive waste storage?
Radioactive waste storage facilities are designed to minimize environmental impact through careful site selection, waste treatment, and monitoring.