Delving into quiz 3 triangles and trigonometry, this comprehensive guide unravels the intricacies of this fascinating mathematical field. From exploring the diverse types of triangles to unlocking the secrets of trigonometric ratios, this quiz empowers you to navigate the complexities of trigonometry with confidence.
As we embark on this mathematical journey, we will delve into the practical applications of trigonometry, uncovering its indispensable role in fields such as engineering, architecture, and navigation. Throughout this quiz, you will encounter engaging examples, insightful explanations, and thought-provoking questions designed to enhance your understanding and appreciation of trigonometry.
1. Types of Triangles
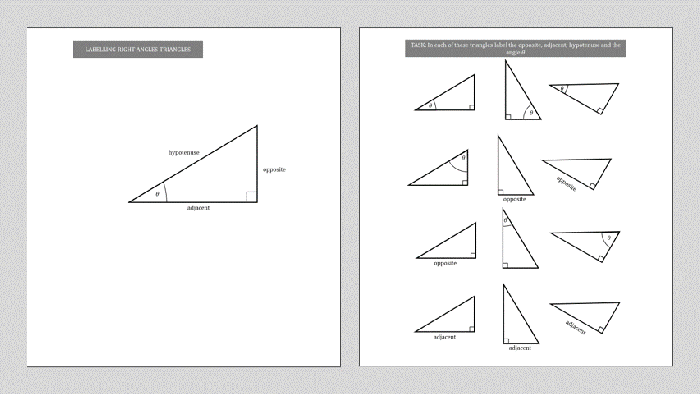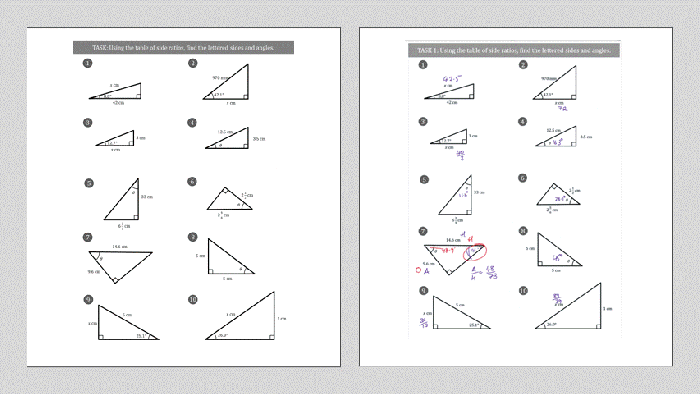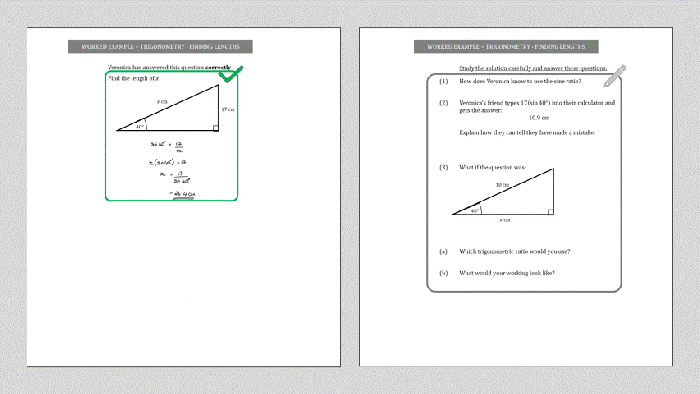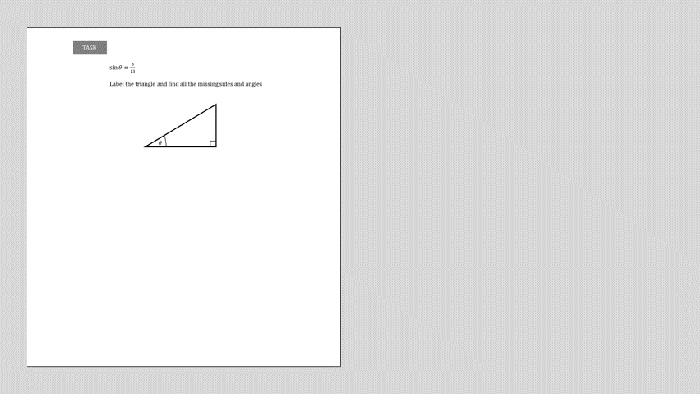
Triangles are classified based on the measures of their angles and the lengths of their sides. Here are the different types of triangles:
1.1. Based on Angles
- Acute Triangle:All three angles are less than 90 degrees.
- Right Triangle:One angle is exactly 90 degrees.
- Obtuse Triangle:One angle is greater than 90 degrees.
1.2. Based on Sides
- Equilateral Triangle:All three sides are equal.
- Isosceles Triangle:Two sides are equal.
- Scalene Triangle:All three sides are different.
1.3. Properties and Characteristics
Each type of triangle has specific properties and characteristics:
- Acute Triangle:The sum of the angles is 180 degrees.
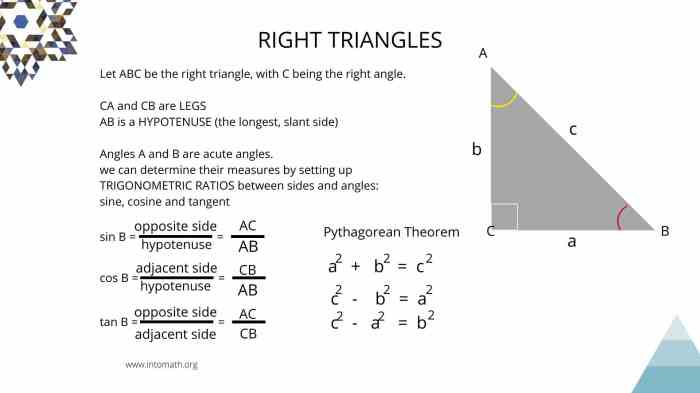
- Right Triangle:The Pythagorean Theorem applies (a 2+ b 2= c 2).
- Obtuse Triangle:The sum of the angles is greater than 180 degrees.
- Equilateral Triangle:All angles are 60 degrees.
- Isosceles Triangle:The angles opposite the equal sides are equal.
- Scalene Triangle:No two angles or sides are equal.
2. Trigonometric Ratios
Trigonometric ratios are functions that relate the sides and angles of a right triangle. The three main trigonometric ratios are:
2.1. Sine (sin)
Sine is defined as the ratio of the length of the opposite side to the length of the hypotenuse.
sin θ = opposite / hypotenuse
2.2. Cosine (cos)
Cosine is defined as the ratio of the length of the adjacent side to the length of the hypotenuse.
cos θ = adjacent / hypotenuse
2.3. Tangent (tan)
Tangent is defined as the ratio of the length of the opposite side to the length of the adjacent side.
tan θ = opposite / adjacent
2.4. Relationships between Trigonometric Ratios
The trigonometric ratios are related by the following identities:
- sin 2θ + cos 2θ = 1
- tan θ = sin θ / cos θ
3. Solving Trigonometric Equations
Solving trigonometric equations involves finding the values of the variable that satisfy the equation. The steps involved are:
3.1. Isolate the Trigonometric Ratio
First, isolate the trigonometric ratio on one side of the equation.
3.2. Find the Reference Angle
Determine the reference angle, which is the angle between 0 and 90 degrees that is equivalent to the given angle.
3.3. Use the Inverse Trigonometric Function
Apply the inverse trigonometric function (e.g., sin -1, cos -1, tan -1) to both sides of the equation to find the value of the variable.
3.4. Consider Multiple Solutions
Trigonometric equations may have multiple solutions due to the periodic nature of the trigonometric functions.
4. Applications of Trigonometry
Trigonometry has numerous applications in various fields, including:
4.1. Navigation
Trigonometry is used to determine the position of ships and aircraft by measuring angles and distances.
4.2. Surveying
Trigonometry is used to measure distances and angles in surveying land and buildings.
4.3. Engineering
Trigonometry is used in structural engineering to design bridges, buildings, and other structures.
4.4. Architecture
Trigonometry is used to calculate angles and distances in architectural design.
4.5. Astronomy, Quiz 3 triangles and trigonometry
Trigonometry is used to calculate distances to stars and planets.
5. Historical Development of Trigonometry: Quiz 3 Triangles And Trigonometry
Trigonometry has a rich history, with its origins dating back to ancient times:
5.1. Ancient Greece
The earliest known trigonometric tables were developed by Hipparchus of Nicaea in the 2nd century BC.
5.2. Islamic Golden Age
Trigonometry was further developed by Muslim mathematicians during the Islamic Golden Age, particularly by Al-Khwarizmi and Al-Battani.
5.3. Renaissance and Enlightenment
In the 16th and 17th centuries, European mathematicians like Regiomontanus and Tycho Brahe made significant contributions to trigonometry.
5.4. Modern Era
In the 19th century, the invention of the calculator and computer greatly simplified trigonometric calculations.
Essential FAQs
What are the different types of triangles?
Triangles can be classified based on their angles (acute, right, obtuse) or sides (scalene, isosceles, equilateral).
How do I calculate trigonometric ratios?
Trigonometric ratios (sine, cosine, tangent) are calculated using the ratios of sides in a right triangle.
What are the applications of trigonometry?
Trigonometry finds applications in navigation, surveying, engineering, architecture, and many other fields.